Evaluación De La Osteointegración De Implantes Trabeculares De Titanio Fabricados Con Tecnología De Metal Poroso: Un Estudio Experimental
Resumen
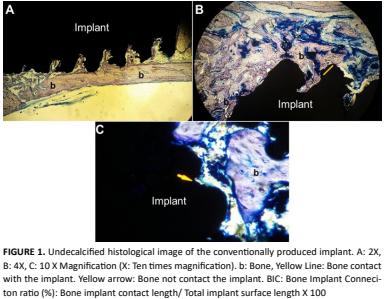
Los implantes de titanio trabecular (TM) producidos con tecnología de metal poroso se utilizan en tratamientos de implantes dentales debido a su semejanza con el hueso esponjoso y sus propiedades físicas y mecánicas. El objetivo de este estudio fue comparar los niveles de conexión hueso- implante (BIC) de los implantes TM con los de los implantes de superficie mecanizada producidos convencionalmente en fémur de rata mediante métodos histológicos. Se utilizaron veinte ratas Sprague-Dawley macho adultas sanas en el estudio. Las ratas se dividieron en 2 grupos iguales: controles e implantes TM. Los implantes se colocaron quirúrgicamente en los huesos del fémur derecho de todas las ratas. Se realizó una incisión curva de aproximadamente 10-15 mm de largo en el aspecto anterolateral de la rodilla derecha. Se diseccionó la cápsula de la articulación de la rodilla formada por el fémur y la tibia. Después de este procedimiento, se subluxó la rótula y se expuso la fosa intercondilar del fémur para la colocación del implante. Después de un período de curación de 4 semanas, se realizaron análisis histomorfométricos no descalcificados de las muestras. Se realizaron mediciones de BIC (%) en las evaluaciones histomorfométricas. Los datos se compararon utilizando la prueba t de Student. El porcentaje promedio de BIC (%) se registró en 37,13% en implantes TM y 29,13% en implantes cilíndricos estándar, y se detectó una diferencia estadísticamente significativa entre los grupos (P <0,05). Dentro de las limitaciones de este estudio, se encontró que los implantes de titanio producidos con tecnología TM tenían porcentajes de BIC más altos que los implantes de titanio cilíndricos estándar.
Descargas
Citas
Yang BC, Zhou XD, Yu HY, Wu Y, Bao CY, Man Y, Cheng L, Sun Y. Advances in titanium dental implant surface modification. West China Journal of Stomatology. [Internet]. 2019; 37(2):124-129. doi: https://doi.org/g65h4g
Alghamdi HS, Jansen JA. The development and future of dental implants. Dent. Mater. J. [Internet]. 2020; 39(2):167-172. doi: https://doi.org/gqnkzm
Albrektsson T, Buser D, Sennerby L. Crestal bone loss and oral implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. [Internet]. 2012; 14(6):783-791. doi: https://doi.org/f22q7f
Buser D, Sennerby L, De Bruyn H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol. 2000. [Internet]. 2017; 73(1):7-21. doi: https://doi.org/f3t8sz
Annunziata M, Guida L. The Effect of Titanium Surface Modifications on Dental Implant Osseointegration. Front. Oral Biol. [Internet]. 2015; 17:62-77. doi: https://doi.org/pzwk
Le Guehennec L, Goyenvalle E, Lopez-Heredia MA, Weiss P, Amouriq Y, Layrolle P. Histomorphometric analysis of the osseointegration of four different implant surfaces in the femoral epiphyses of rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2008; 19(11):1103-1110. doi: https://doi.org/bxgbv2
Le Guéhennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P, Amouriq Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. [Internet]. 2007; 23(7):844-854. doi: https://doi.org/b2rw2d
Dundar S, Yaman F, Gecor O, Cakmak O, Kirtay M, Yildirim TT, Karaman T, Benlidayi ME. Effects of Local and Systemic Zoledronic Acid Application on Titanium Implant Osseointegration: An Experimental Study Conducted on Two Surface Types. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2017; 28(4):935-938. doi: https://doi.org/gbh973
Smeets R, Stadlinger B, Schwarz F, Beck-Broichsitter B, Jung O, Precht C, Kloss F, Gröbe A, Heiland M, Ebker T. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Osseointegration. Biomed. Res. Int. [Internet]. 2016; 2016:6285620. doi: https://doi.org/f9jp5f
Stanford CM. Surface modifications of dental implants. Aust Dent J. [Internet]. 2008; 53(Suppl1):S26-S33. doi: https://doi.org/bgsg5v
Bencharit S, Byrd WC, Altarawneh S, Hosseini B, Leong A, Reside G, Morelli T, Offenbacher S. Development and applications of porous tantalum trabecular metal- enhanced titanium dental implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. [Internet]. 2014; 16(6):817-826. doi: https://doi.org/gp3dgq
Velasco-Ortega E, Ortiz-Garcia I, Jiménez-Guerra A, Núñez-Márquez E, Moreno-Muñoz J, Rondón-Romero JL, Cabanillas-Balsera D, Gil J, Muñoz-Guzón F, Monsalve- Guil L. Osseointegration of Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Implant Surfaces. A Histological and Histomorphometric Study in the Rabbit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. [Internet]. 2021; 22(16):8507. doi: https://doi.org/gp5nmb
Yeo IL. Modifications of Dental Implant Surfaces at the Micro- and Nano-Level for Enhanced Osseointegration. Materials. [Internet]. 2020; 13(1):89. doi: https://doi.org/gmwpwg
Blatt S, Pabst AM, Schiegnitz E, Hosang M, Ziebart T, Walter C, Al-Nawas B, Klein MO. Early cell response of osteogenic cells on differently modified implant surfaces: Sequences of cell proliferation, adherence and modified implant surfaces: Sequences of cell proliferation, adherence and differentiation. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2018; 46(3):453-460. doi: https://doi.org/gc4zdt
Luke Yeo IS. Dental Implants: Enhancing Biological Response Through Surface Modifications. Dent. Clin. North. Am. [Internet]. 2022; 66(4):627-642. doi: https://doi.org/gtq9h2
Romanos GE, Delgado-Ruiz RA, Sacks D, Calvo-Guirado JL. Influence of the implant diameter and bone quality on the primary stability of porous tantalum trabecular metal dental implants: an in vitro biomechanical study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2018; 29(6):649-655. doi: https://doi.org/pzwn
Bencharit S, Morelli T, Barros S, Seagroves JT, Kim S, Yu N, Byrd K, Brenes C, Offenbacher S. Comparing Initial Wound Healing and Osteogenesis of Porous Tantalum Trabecular Metal and Titanium Alloy Materials. J. Oral. Implantol. [Internet]. 2019; 45(3):173-180. doi: https://doi.org/pzwp
de Arriba CC, Alobera Gracia MA, Coelho PG, Neiva R, Tarnow DP, Del Canto Pingarron M, Aguado-Henche S. Osseoincorporation of Porous Tantalum Trabecular- Structured Metal: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in Humans. Int. J. Periodontics Restorative Dent. [Internet]. 2018 [cited 05 Apr 2025]; 38(6):879–885. Available in: https://goo.su/Ucon1
Özcan EC, Aydin MA, Dundar S, Tanrisever M, Bal A, Karasu N, Kirtay M. Biomechanical Investigation of the Osseointegration of Titanium Implants With Different Surfaces Placed With Allogeneic Bone Transfer. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2024; 35(7):2184-2188. doi: https://doi.org/pmwx
Al Deeb M, Aldosari AA, Anil S. Osseointegration of Tantalum Trabecular Metal in Titanium Dental Implants: Histological and Micro-CT Study. J. Funct. Biomater. [Internet]. 2023; 14(7):355. doi: https://doi.org/pzwr
Dundar S, Yaman F, Bozoglan A, Yildirim TT, Kirtay M, Ozupek MF, Artas G. Comparison of Osseointegration of Five Different Surfaced Titanium Implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2018; 29(7):1991-1995. doi: https://doi.org/pmw5
Calvo-Guirado JL, Satorres-Nieto M, Aguilar-Salvatierra A, Delgado-Ruiz RA, Maté-Sánchez de Val JE, Gargallo- Albiol J, Gómez-Moreno G, Romanos GE. Retraction Note: Influence of surface treatment on osseointegration of dental implants: histological, histomorphometric and radiological analysis in vivo. Clin. Oral Investig. [Internet]. 2024; 28(1):118. doi: https://doi.org/pzws
Kreve S, Ferreira I, da Costa Valente ML, Dos Reis AC. Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: a systematic review. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2024; 28(1):1-14. doi: https://doi.org/pzwt
Lee JW, Wen HB, Battula S, Akella R, Collins M, Romanos GE. Outcome after placement of tantalum porous engineered dental implants in fresh extraction sockets: a canine study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. [Internet]. 2015 [cited 05 Apr 2025]; 30(1):134-142. Available in: https://goo.su/4Sps0
Gasbarra E, Iundusi R, Perrone FL, Saturnino L, Tarantino U. Densitometric evaluation of bone remodelling around Trabecular Metal Primary stem: a 24-month follow-up. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. [Internet]. 2015; 27(Suppl 1):S69-S75. doi: https://doi.org/pzww
Fraser D, Mendonca G, Sartori E, Funkenbusch P, Ercoli C, Meirelles L. Bone response to porous tantalum implants in a gap-healing model. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2019; 30(2):156-168. doi: https://doi.org/gx7ksq
Lee JW, Wen HB, Gubbi P, Romanos GE. New bone formation and trabecular bone microarchitecture of highly porous tantalum compared to titanium implant threads: A pilot canine study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2018; 29(2):164-174. doi: https://doi.org/gts25s