El efecto del mineral boro sobre el metabolismo energético y la actividad antioxidante en potros árabes de pura raza
Resumen
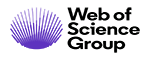
Se ha comprobado que el mineral boro desempeña funciones significativas en el metabolismo lipídico y energético, los sistemas inmunitario y endocrino, y la actividad cerebral, ejerciendo un impacto positivo en el rendimiento. El objetivo del presente estudio fue investigar los efectos de diferentes dosis de boro mineral (0, 5, 10, 15 mg·d-1·animal-1) sobre el metabolismo energético y los parámetros de actividad antioxidante en potros árabes de pura raza a los 30, 60 y 90 días. El ensayo se llevó a cabo en un total de 32 potros, agrupados aleatoriamente con base en su peso corporal inicial, conformando 8 potros por grupo (n=8). Los grupos experimentales se definieron en función de las dosis de boro mineral administradas. El grupo de control (Grupo K) no recibió boro, el Grupo B5 recibió 5 mg de boro elemental, el Grupo B10 recibió 10 mg y el Grupo B15 recibió 15 mg al día por animal. Se empleó ácido bórico como fuente de boro. El estudio tuvo una duración de 90 días. Se observó que el consumo de pienso y el aumento de peso corporal fueron similares en todos los grupos (P>0,05). Durante el transcurso del estudio, no se observaron diferencias significativas en los niveles séricos de glucosa, colesterol, triglicéridos, AST y ALT entre los grupos (P>0,05). Se observó una disminución dependiente de la dosis en los niveles de MDA tras lasmediciones iniciales (P<0,001), mientras que los niveles de GSH–Px y CAT aumentaron de forma dependiente de la dosis tras las mediciones iniciales (P<0,001). En conclusión, el boro mineral afectó positivamente a la actividad antioxidante de los potros árabes de pura raza, siendo la dosis más eficaz la de 15 mg·d-1·animal-1.
Descargas
Citas
World Health Organization (WHO). International Programme on Chemical Safety. Environmental Health Criteria 204 Boron. [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization.; 1998 [cited Feb 23, 2025]; 224 p. Available in: https://shre.ink/t4Cb
Eren M. Bor’un biyolojik önemi ve metabolizma üzerine etkileri [Effects on metabolism and biological importance of boron]. Erciyes Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. [Internet]. 2004 [cited Jan 12, 2025]; 1(1):55-59. Turkish. Available in: https://shre.ink/t4XO
Kabu M, Civelek T. Effects of propylene glycol, methionine and sodium borate on metabolic profile in dairy cattle during periparturient period. Revue Méd. Vét. [Internet]. 2012 [cited Jan 14, 2025]; 163(8-9):419-430. Available in: https://shre.ink/t4Xy
Hunt CD. Dietary boron: Progress in establishing essential roles in human physiology. J Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2012; 26(2-3):157-160. Turkish. doi: https://doi.org/f32wd7
Yeşilbağ D. Hayvan beslemede bor elementinin kullanımı [The use of boron in animal nutrition]. Uludag Univ. J. Fac. Vet. Med. [Internet]. 2008 [cited Feb 12, 2025]; 27(1-2): 61-68. Turkish. Available in: https://shre.ink/t4Xq
Hunt CD. Regulation of enzymatic activity: One possible role of dietary boron in higher animals and humans. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. [Internet]. 1998 [cited Feb. 3, 2025]; 66:205–225. Available in: https://shre.ink/t4Xr
Abdelnour SA, El–Hack MEA, Swelum AA, Perillo A, Losacco C. The vital roles of boron in animal health and production: A comprehensive review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2018; 50:296-304. doi: https://doi.org/gfm5s4
Bakken NA, Hunt CD. Dietary boron decrease peak pancreatic in situ insülin release inchicks and plasm insulin concentration in rats regardless of vitamin D or magnesium status. J. Nutr. [Internet]. 2003; 133(11):3577-3583. doi: https://doi.org/pzd5
Devirian TA, Volpe SL. The physiological effects of dietary boron. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. [Internet]. 2003; 43(2):219-231. doi: https://doi.org/cjjtnt
Bast A, Goris RJ. Oxidative stress: Biochemistry and human disease. Pharm. Weekbl. Sci. [Internet]. 1989; 11(6):199-206. doi: https://doi.org/cbqz54
Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Cigerci H, Fatih Fidan A, Eryavuz A. The effects of dietary boric acid and borax supplementation on lipid peroxidation. antioxidant activity and DNA damage in rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2010; 24(3):161-164. doi: https://doi.org/c567nz
Coban FK, Ince S, Kucukkurt I, Demirel HH, Hazman O. Boron attenuates malathion–induced oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2015; 38(4):391-399. doi: https://doi.org/pzd6
Bhasker TV, Gowda NK, Mondal S, Krishnamoorthy P, Pal DT, Mor A, Karthik Bhat S, Pattanaik AK. Boron influences immune and antioxidant responses by moduling hepatic superoxide dismutase activity under calcium deficit abiotic stress in Wistar rats. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2016; 36:73-79. doi: https://doi.org/f8vn39
Kurtoglu, Kurtoglu F, Akalın PP. The effect of various levels of boron supplementation on live weight plasma lipid peroxidation. several biochemical and tissue antioxidant parameters of male mice: Effects of boron on performance. antioxidant and some metabolites of mice. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2018; 49:146-150. doi: https://doi.org/gdxsg6
Pawa S, Ali S. Boron ameliorates fulminant hepatic failure by counteracting the changes associated with the oxidative stress. Chem. Biol. Interact. [Internet]. 2006; 160(2):89–98. doi: https://doi.org/fjfp7s
Basoglu A, Baspinar N, Ozturk AS, Akalin PP. Effects of long– term boron administration on high–energy diet–induced obesity in rabbits: NMR–based metabonomic evaluation. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. [Internet]. 2011; 10(12):1512-1515. doi: https://doi.org/dnrb9c
Eren M, Uyanik F, Küçükersan S. The influence of dietary boron supplementation on egg quality and serum calcium. inorganic phosphorus. magnesium levels and alkaline phosphatase activity in laying hens. Res. Vet. Sci. [Internet]. 2004; 76(3):203-210. doi: https://doi.org/fpnc2z
Khaliq H, Jing W, Ke X, Ke–Li Y, Peng–Peng S, Wei wei Q, Zhixin L, Hua–Zhen L, Hui S, Ju–Ming Z, Ke–Mei P. Boron affects the development of the kidney through modulation of apoptosis. antioxidant capacity. and Nrf2 pathway in the African ostrich chicks. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. [Internet]. 2018; 186(1):226-237. doi: https://doi.org/gfhbwc
National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Horses. 6th rev. ed. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2007. doi: https://doi.org/pzhh
Rondanelli M, Falivac MA, Peronic G, Infantinob V, Gasparric C, Iannello G, Perna S, Riva A, Petrangolini G, Tartara A. Pivotal role of boron supplementation on bone health: A narrative review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2020; 62:126577. doi: https://doi.org/pzhj
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Opinion of the scientific panel on dietetic products. nutrition and allergies on a request from the commission related to the tolerable upper intake level of boron (sodium borate and boric acid). EFSA J. [Internet]. 2004 [cited Jan 18, 2025]; 2(8):80. Available in: https://goo.su/qPlA
Horwitz W. Official Methods of Analysis Association of Official Agricultural Chemist. 13th ed. Washington D.C. : Association of Official Analytical Chemists; 1980.
Crampton EW, Maynard LA. The relation of cellulose and lignin content to nutritive value of animal feeds. J Nutr. [Internet]. 1938; 15(4):383-395. doi: https://doi.org/pzhk
Coşkun B, İnal F, İnal Ş. Ration Programs. At_V5.05. 2019. Selçuklu–Konya (Türkiye): Selçuk Üniversitesi, Zootekni Ve Hayvan Besleme.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Internet]. 2024 [cited April 24, 2025]. Available in: https://www.epa.gov/
Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE. Tietz Textbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics. 5th ed. St. Louis (Missouri, USA): Elsevier Saunders. [Internet]. 2014 [cited July 04, 2025] Available in: https://goo.su/oHX6E
Placer AZ, CushmanLL, Johnson BC. Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyldialdehyde) in biochemical systems. Anal. Biochem. [Internet]. 1966; 16(2):359-364. doi: https://doi.org/b96rpj
Goth L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin. Chim. Acta. [Internet]. 1991; 196(2-3):143-151. doi: https://doi.org/fthsdb
Lawrence R, Burk R. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium–deficient rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. [Internet]. 1976; 71(4):952-958. doi: https://doi.org/d3vv59
IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0. Armonk, (NY, USA): IBM Corp; 2013. Available in: https://goo.su/VQgSI3
Cakir S, Eren M, Sentürk M, Sarıca ZS. The effect of boron on some biochemicals parameters in experimental diabetic rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. [Internet]. 2018; 184(1):165-172. doi: https://doi.org/gdqq5s
Hunt CD. Dietary boron modified the effects of magnesium and molybdenum on mineral metabolism in the cholecalciferol deficient chick. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. [Internet]. 1989; 22(2):201-220. doi: https://doi.org/bpmnxw
Hunt CD, Herbel JL. Effects of dietary boron on calcium and mineral metabolism in the streptozotocin–injected vitamin d3 deprived rat. Magnes. Trace Elem. [Internet]. 1991 [cited Feb 13, 2025]; 10(5-6):387-408. Available in: https://goo.su/NuPf
Eren M, Uyanik F, Guclu BK, Atasever A. The influence of dietary boron supplementation on performance. some biochemical parameters and organs in broilers. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. [Internet]. 2012; 7(11):1079-1089. doi: https://doi.org/pzhp
Eren M, Uyanik F. Influence of dietary boron supplementation on some serum metabolites and egg–yolk cholesterol in laying hens. Acta Vet. Hung. [Internet]. 2007; 55(1):29-39. doi: https://doi.org/cxnvjt
Hall LH, Spielvogal BF, Griffin TS, Docks EL, Brotherton RJ. The effects of boron hyperlipidemicagents on LDL and HDL receptor binding and related enzyme activities of rat hepatocytes, aorta cells and human fibroblasts. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 1989 [cited Dec 16, 2024]; 65(3):297–317. Available in: https://goo.su/wUIWz
Kurtoğlu F, Kurtoğlu V, Çelik İ, Keçeci T, NizamLıoğlu M. Effects of dietary boron supplementation on some biochemical parameters, peripheral blood lymphocyte, splenic plasma cells and bone characteristics of broiler chicks given diets with adequate or ınadequate cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) content. Br. Poult. Sci. [Internet]. 2005; 46(1):87-96. doi: https://doi.org/dtkvnb
Eren M, Kocaoglu Güclü B, Uyanık F, Karabulut N. The effects of dietary boron supplementation on performance. carcass composition and serum lipids in Japanese quails. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. [Internet]. 2006 [cited Feb. 18, 2025]; 5(12):1105- 1108. Available in: https://goo.su/WC5Z2
Anurag L, Aniket S, Shalik J, Amarja L, Dhananjay R, Sachin J. Non–alcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence and associated risk factors–A study from rural sector of Maharashtra. Trop. Gastroenterol. [Internet]. 2015; 36(1):25-30. doi: https://doi.org/gs8rsm
Ezhilarasan D. Oxidative stress is bane in chronic liver diseases: Clinical and experimental perspective. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. [Internet]. 2018; 19(2):56-64. doi: https://doi.org/pzhx
Kikusato M, Nakamura K, Mikami Y, Mujahid A, Toyomizu M. The suppressive effect of dietary coenzyme Q10 on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production and oxidative stress in chickens exposed to heat stress. Anim. Sci. J. [Internet]. 2016; 87(10):1244-1251. doi: https://doi.org/f89g92
Azad MAK, Kikusato M, Zulkifli I, Toyomizu M. Electrolysed reduced water decreases reactive oxygen species induced oxidative damage to skeletal muscle and improves performance in broiler chicken sex posed to medium–termchronic heat stress. Br. Poult. Sci. [Internet]. 2013; 54(4):503-509. doi: https://doi.org/pzhz